AlNahdaElectronics1
Electronics1
ELECTRICITY is... What??
A flow of ELECTRONS.
So, WHERE DO ELECTRONS COME FROM ?? and,
WHERE DO ELECTRONS GO??? AND WHAT DO THEY LOOK LIKE??
ANYWAY.. It works like this:
Electrons come from SOURCES and go to LOADS.
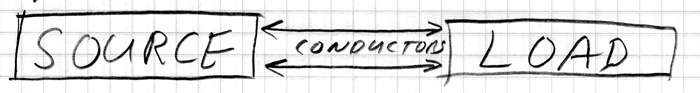
Examples:
- The 220 Volt AC power in a wall outlet SOURCE goes to a 100 Watt Light Bulb LOAD.
- The 12 Volt DC power from a car battery SOURCE goes to a 20 watt Tail Light Bulb LOAD.
- The 1.5 Volt DC power from the dry cell SOURCE in a flashlight goes to a 1/2 watt LED Flashlight Bulb LOAD.
- The 3.7 Volt DC power from a Lithium Ion Battery SOURCE goes to a Digital Camera LOAD.
IMPORTANT ! !
LOADS must be matched to appropriate SOURCES or Bad Stuff Happens:
- The LOAD doe not work properly, or at all. OR,
- Ka-BOOM ! ! The LOAD is damaged or destroyed
CIRCUITS:
CIRCUITS connect SOURCES and LOADS together with CONDUCTORS. CONDUCTORS are usually wires, but may be any other conductive material such as a metal strap, the metal case of a flashlight, etc.
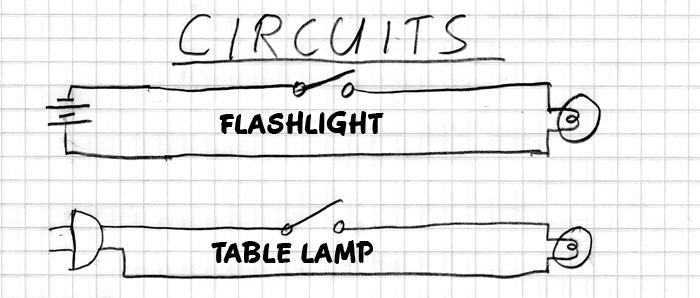
CIRCUITS can be simple, like a flashlight with one SOURCE connected in a circuit with one LOAD. Or, they can be very complex, like the wiring of Stage Lights, with many sources and many loads. Or they can be wicked complex, like a Pentium processor chip, with many millions of sources and loads.
We need to look at BASICS
Let's look at this example:
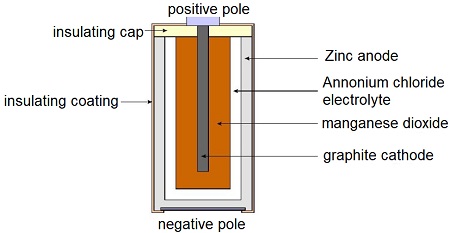
SOURCES of electricity: DRY CELL
A standard dry cell comprises a zinc anode, usually in the form of a cylindrical pot, with a carbon cathode in the form of a central rod. The electrolyte is ammonium chloride in the form of a paste next to the zinc anode.
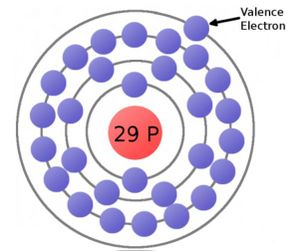
WIRES - Conductivity
Wires are are usually made of Copper or Aluminum. Their Atoms are Conductive. The outer most shell for a given atom is called the valence shell. The conductivity of the atom depends on the number of electrons that are in the valence shell.
- If the outer shell is FULL there are no Free Electrons. It is an INSULATOR
- If the outer shell is not full there are Free Electrons. It is a CONDUCTOR
LIGHTS
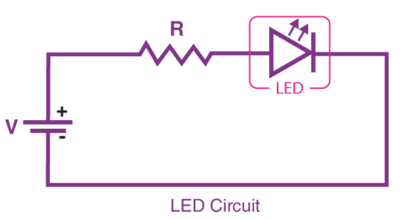
- Incandescent bulb - Hot wire glows - - LED (Light Emitting Diode) - Emits light from semiconductor surface
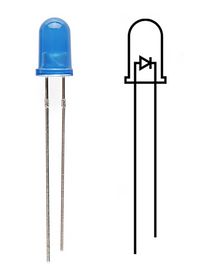 LED Long wire is +
LED Long wire is +
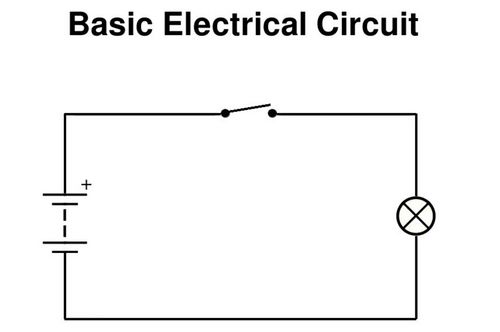
ELECTRICAL CIRCUIT
SOURCE connected to LOAD
SWITCHES
Connect or DISconnect SOURCES from LOADS.